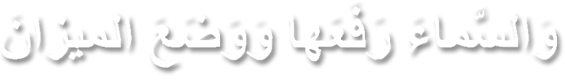Salah
Salah
Salah is the Arabic word for prayer, and it is one of the five pillars of Islam. Muslims perform Salah five times a day, as a way to connect with Allah (God) and fulfill their spiritual obligations. Each Salah consists of a series of physical postures and recitations, including standing, bowing, prostrating, and sitting. During Salah, Muslims recite verses from the Quran, and they may also supplicate to Allah in their own words.
Salah is performed facing the Kaaba in Mecca, and it is typically performed in congregation at a community centre, although it can also be performed individually. The five daily Salah are Fajr (pre-dawn), Dhuhr (midday), Asr (afternoon), Maghrib (sunset), and Isha (nighttime). The timing of each Salah is determined by the position of the sun, and Muslims are expected to perform Salah at the prescribed times, regardless of their location or circumstances.
Salah is considered a form of worship and a way to seek forgiveness and guidance from Allah. It is an important part of a Muslim's daily life and serves as a reminder of the ultimate purpose of life and the importance of submitting to Allah's will. Through Salah, Muslims seek to strengthen their relationship with Allah and to become more mindful of their duties and responsibilities as Muslims.